Outrageous Aerobic Respiration Chemical Formula
Aerobic respiration is a fixed metabolic reaction that takes place in the presence of oxygen going on in a cellular to transform chemical energy into ATPs.
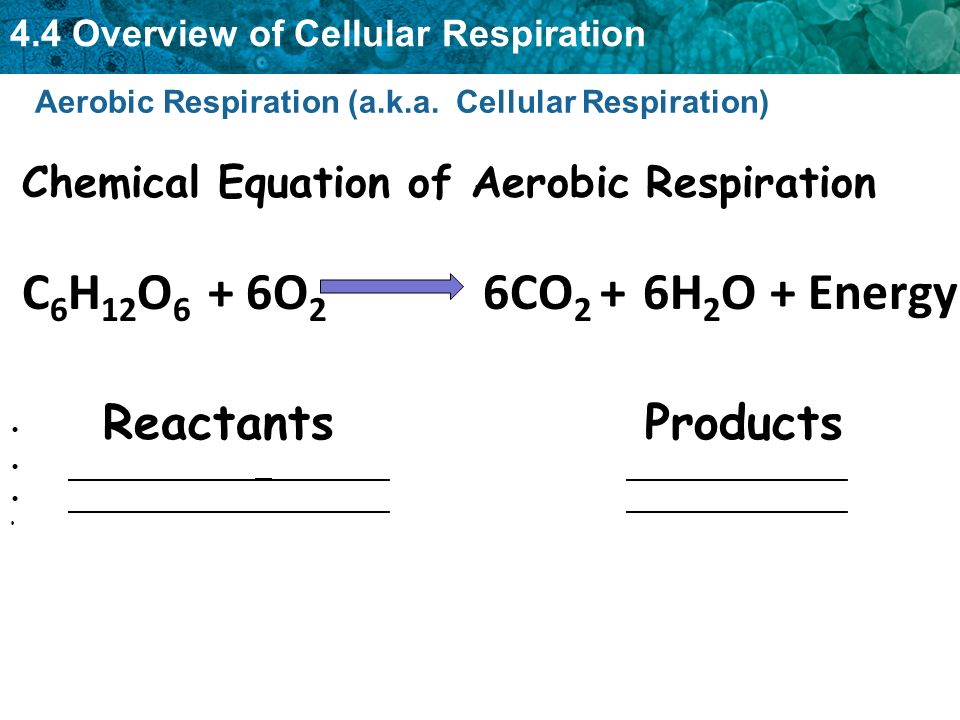
Aerobic respiration chemical formula. When the four ATP produced in glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle are added the total of 38 ATP fits the overall equation for aerobic cellular respiration. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate.
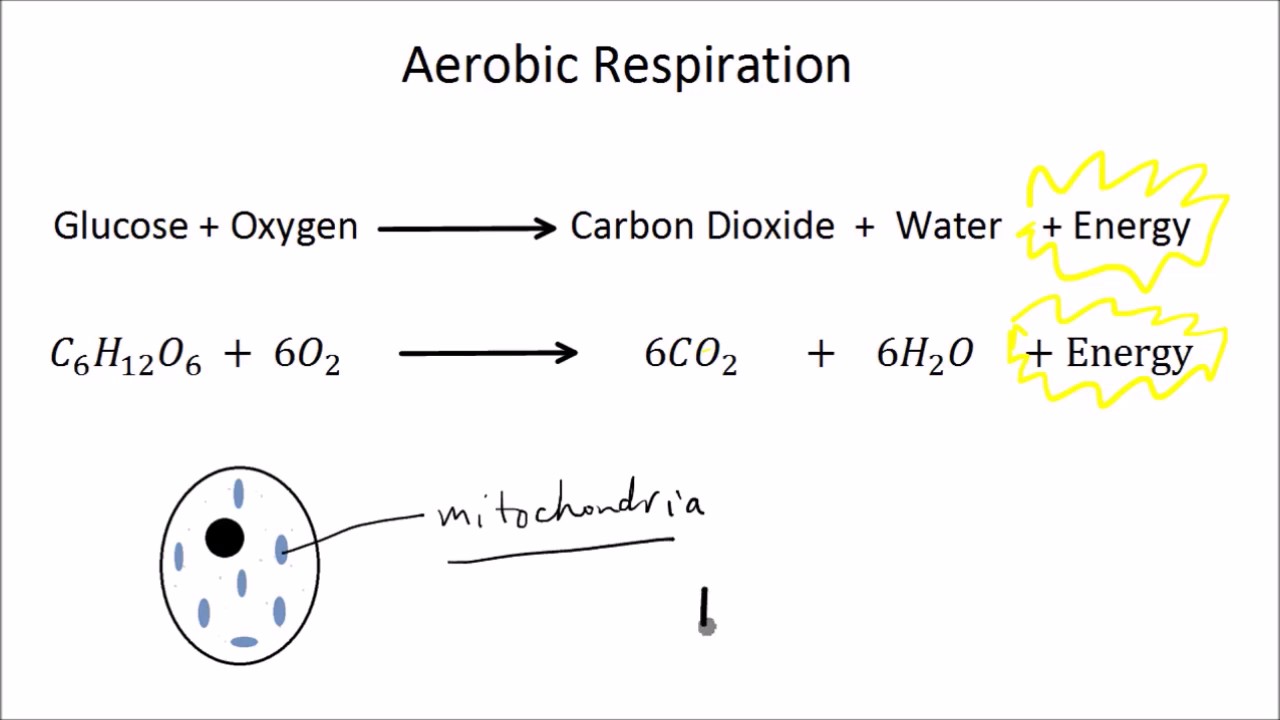
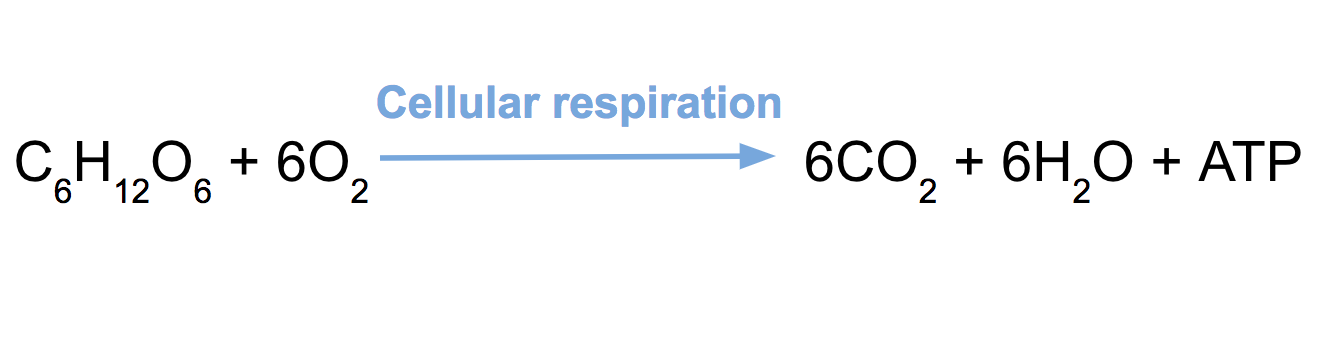
Aerobic respiration on the other hand sends the pyruvate leftover from glycolysis down a very different chemical path the steps of which are discussed in detail below. C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2 yields 6CO 2 6H 2 O energy as ATP. This is the currently.
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. C6H12O6 6O2 -------------------à 6CO2 6H2O 2900 kJmol This equation also showcases the process of aerobic respiration and tells us that energy of about 2900 kJ is generated when a single mole. The energy released via aerobic respiration helps plants and animals including us grow.
Aerobic respiration is the aerobic catabolism of nutrients to carbon dioxide water and energy and involves an electron transport system in which molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor. Aerobic respiration is a biological process in which food glucose is converted into energy in the presence of oxygen. The equation for aerobic respiration describes the reactants and products of all of its steps including glycolysis.
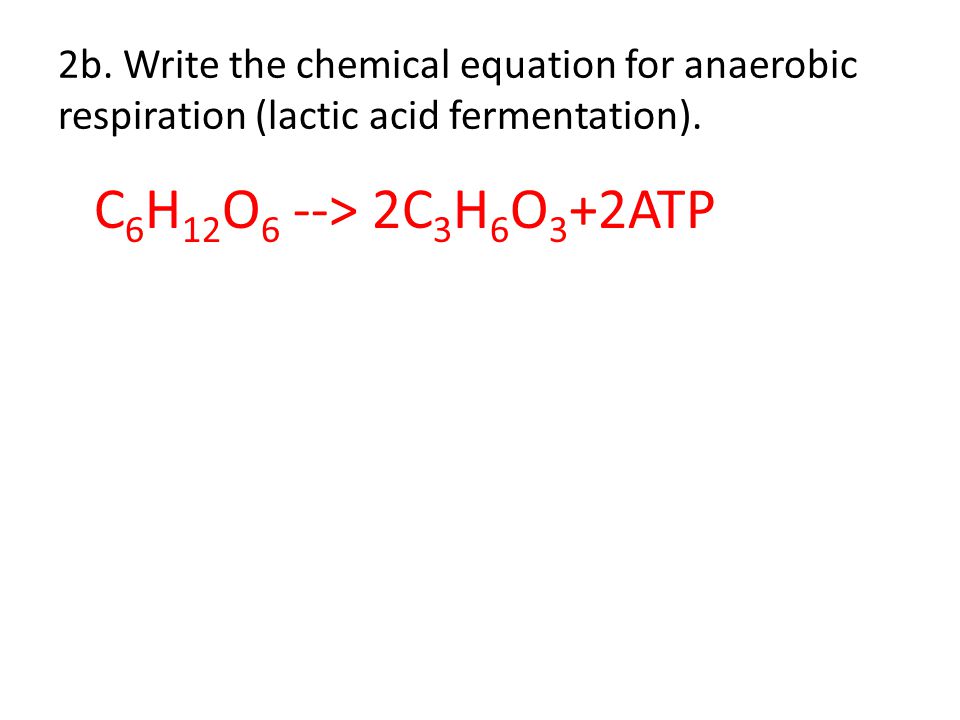
In aerobic respiration glucose breaks down producing carbon dioxide while oxygen combines with other small products of this process to form water. Write the overall chemical equations of the two kinds of respiration in plants. Anaerobic respiration is a process of cellular respiration in which the excessive energy electron acceptor is neither oxygen nor pyruvate derivatives.
The process can be simply explained with the help of the following equation. Aerobic respiration is a process used by organisms such as humans to convert organic fuels in food such as carbohydrates into chemical energy in the presence of oxygen. An example of the aerobic respiration equation is in figure 3.