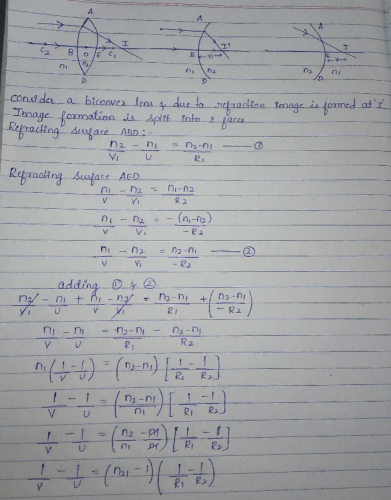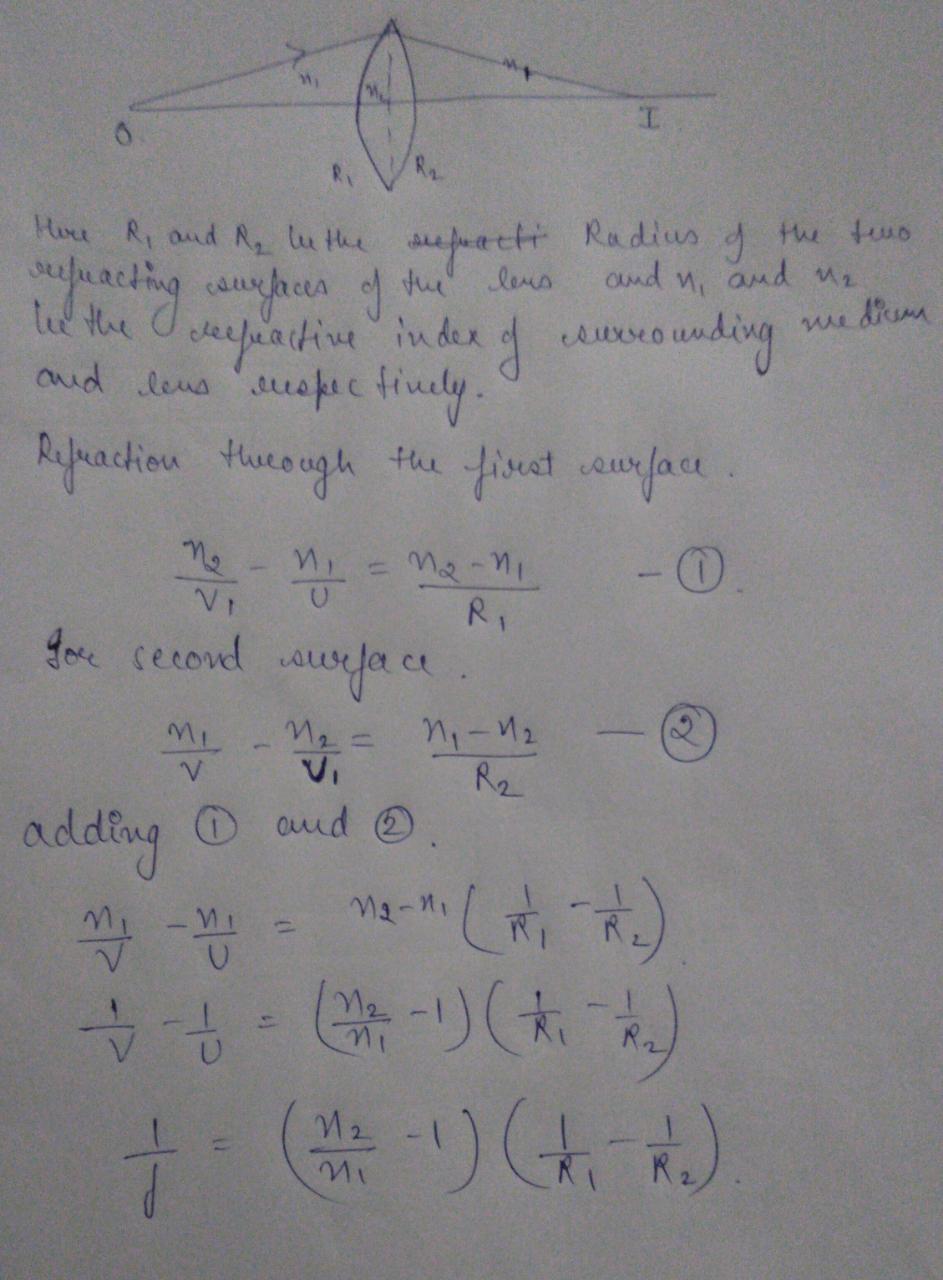Fun Lens Maker Formula Derivation

Lens Maker Formula With Derivation The formula giving the relation between the focal length f of the lens the refractive index of the material of the lens n and the radii of curvature of its surface R 1 R 2 is known as Lens maker formula.
Lens maker formula derivation. Hence obtain the expression for lens-makers formula in the case of thin convex lens. We assume a thin converging lens and that the light rays we are dealing with are close to the principal axis and make very small angles with the principal axis angles of less than 10 o resulting in very small angles of. It is so called because it is used by lens manufacturers to make lenses of particular power from the glass of given refractive index.
Amansinha1253 amansinha1253 25092020 Physics Secondary School 5 pts. The focal length of a lens depends upon. Write the basic assumptions used in the derivation of lens makers formula and hence derive this expression.
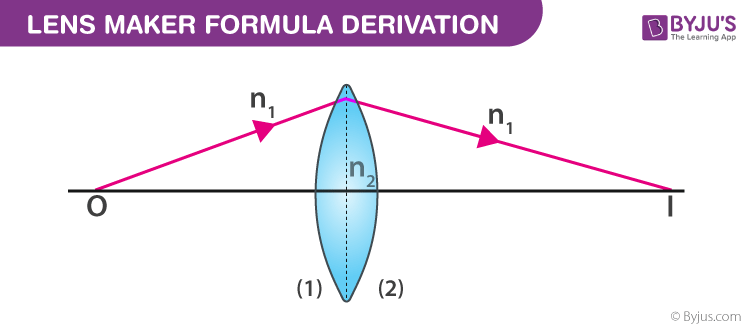
I Aperture of lens should be small ii Lenses should be thin iiiObject should be point sized and placed on principal axis. The lens formula is given below. In this session Tushar sir will be discussing the topic Lens Maker Equations Mirror Formula with practice multiple choice questions from Class 10 Physic.
The Lens Makers Formula Lens manufacturers use the lens makers formula to manufacture lenses of the desired focal length. V distance of the image from the lens. Lenses of different focal lengths are used for different optical instruments.
So to derive the lens makers formula you first need to derive the relation between object and image distance in terms of refractive index of the medium and the radius of curvature of the curved spherical surface. Answered Derive lens maker formula 2. Its not mandatory but it makes the derivation.
If you want me to teach you Biology or Chemistry or Physics. The Lens Makers Formula is an expression used to find the focal length of a lens for which the refractive index as well as the radii of curvature are known. We will discuss the form of the equation that is applicable only to thin lenses.